Views: 13
Create a GRUB password
grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2PBKDF2 stands for Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2.
It is important to note that adding a password for GRUB is not available for systems deployed using cloud service providers (such as our Linux VM); a GRUB password does not make sense as you don’t have access to the physical terminal.
Encryption
There are various software systems and tools that provide encryption to Linux systems.Many modern Linux distributions ship with LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) encryption utility.
sudo lsblk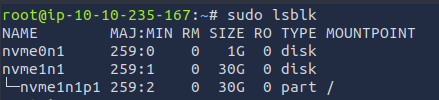
The blkid command allows you to display information about available block devices.

- Install
cryptsetup-luks. (You can issueapt install cryptsetup,yum install cryptsetup-luksordnf install cryptsetup-luksfor Ubuntu/Debian, RHEL/Cent OS, and Fedora, respectively.) - Confirm the partition name using
fdisk -l,lsblkorblkid. (Create a partition usingfdiskif necessary.) - Set up the partition for LUKS encryption:
cryptsetup -y -v luksFormat /dev/sdb1. (Replace/dev/sdb1with the partition name you want to encrypt.) - Create a mapping to access the partition:
cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 EDCdrive. - Confirm mapping details:
ls -l /dev/mapper/EDCdriveandcryptsetup -v status EDCdrive. - Overwrite existing data with zero:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mapper/EDCdrive. - Format the partition:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/EDCdrive -L "Strategos USB". - Mount it and start using it like a usual partition:
mount /dev/mapper/EDCdrive /media/secure-USB.
sudo cryptsetup open --type luks encrypted_filename mount_folder && sudo mount /mount_folderLinux Firewalls
- What can enter? Allow or deny packets from entering a system.
- What can leave? Allow or deny packets from leaving a system.
On a Linux system, a solution such as SELinux or AppArmor can be used for more granular control over processes and their network access. For example, we can allow only the /usr/bin/apache2 binary to use ports 80 and 443 while preventing any other binary from doing so on the underlying system. Both tools enforce access control policies based on the specific process or binary, providing a more comprehensive way to secure a Linux system.
Netfilter
The netfilter project provides packet-filtering software for the Linux kernel 2.4.x and later versions. The netfilter hooks require a front-end such as iptables or nftables to manage.
iptables
As a front-end, iptables provides the user-space command line tools to configure the packet filtering rule set using the netfilter hooks. For filtering the traffic, iptables has the following default chains:
- Input: This chain applies to the packets incoming to the firewall.
- Output: This chain applies to the packets outgoing from the firewall.
- Forward This chain applies to the packets routed through the system.
#Accept incoming packets to TCP port 22
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT appends to the INPUT chain, i.e., packets destined for the system.
-p tcp --dport 22 applies to TCP protocol with destination port 22.
-j ACCEPT specifies (jump to) target rule ACCEPT.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
#Accept outgoing packets from TCP port 22
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT append to the OUTPUT chain, i.e., packets leaving the system.
-p tcp --sport 22 applies to TCP protocol with source port 22.Example, We only want to allow traffic to the local SSH server and block everything else. In this case, we need to add two more rules to set the default behaviour of your firewall:
iptables -A INPUT -j DROPto block all incoming traffic not allowed in previous rules.iptables -A OUTPUT -j DROPto block all outgoing traffic not allowed in previous rules.
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -j DROP
iptables -A OUTPUT -j DROPnftables
nftables is supported in Kernel 3.13 and later, adding various improvements over iptables, particularly in scalability and performance.
Configuration Example: A simple nftables configuration that allows traffic to the local SSH server.
Unlike iptables, nftables start with no tables or chains. We need to add the necessary tables and chains before adding rules. To begin, we need to create a table, fwfilter.
# Create a table
nft add table fwfilter
-->add is used to add a table. Other commands include delete to delete a table, list to list the chains and rules in a table, and flush to clear all chains and rules from a table.
-->table TABLE_NAME is used to specify the name of the table we want to create
# In the newly created table, fwfilter, we will add an input chain and an output chain for incoming and outgoing packets, respectively.
nft add chain fwfilter fwinput { type filter hook input priority 0 \; }
nft add chain fwfilter fwoutput { type filter hook output priority 0 \; }
#The above two commands add two chains to the table fwfilter:
-->fwinput is the input chain. It is of type filter and applies to the input hook.
-->fwoutput is the output chain. It is of type filter and applies to the output hook.
# With the two chains created within our table, we can add the necessary rule to allow SSH traffic. The following two rules are added to the table fwfilter to the chains fwinput and fwoutput, respectively:
nft add fwfilter fwinput tcp dport 22 accept
nft add fwfilter fwoutput tcp sport 22 accept
# To verify the shape of the table (fwfilter)
nft list table fwfilter
UFW
UFW stands for uncomplicated firewall.
ufw allow 22/tcp
# To verify the settings
sudo ufw status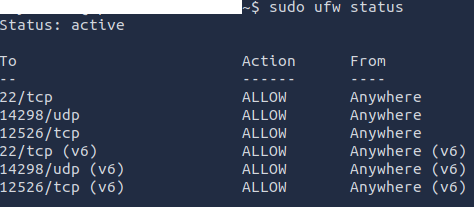
When to use firewalld, nftables, or iptables (Redhat recommendation)
firewalld: Use thefirewalldutility for simple firewall use cases. The utility is easy to use and covers the typical use cases for these scenarios.nftables: Use thenftablesutility to set up complex and performance-critical firewalls, such as for a whole network.iptables: Theiptablesutility on Red Hat Enterprise Linux uses thenf_tableskernel API instead of thelegacyback end. Thenf_tablesAPI provides backward compatibility so that scripts that useiptablescommands still work on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. For new firewall scripts, Red Hat recommends to usenftables.
To prevent the different firewall-related services from influencing each other, run only one of them on a Linux host, and disable the other services.
Firewall Policy
Two common approaches,
- Block everything and allow certain exceptions.
- Allow everything and block certain exceptions.



